Read about the project!
If you want to know even more, you should check out the downloads!
Description
The Parallel Data Transmission project has managed to construct a working massive MIMO system that uses audio waves for communication.
The resulting system consists of a total of 16 units, each containing both a loudspeaker and a microphone, together with a Matlab program that controls these units.
The user can choose to use between 1 and 4 of these loudspeaker/microphone units as terminals, and the rest as part of the MIMO array (corresponding to a base station).
When started, the system is running a massive MIMO communication system with only downlink data. Each frame contains two parts; pilot transmission from the terminals, and downlink data transmission using beamforming.
As such, the system demonstrates that this technique can be used to transmit independent data streams simultaneously to terminals that are separated in space, using the same frequency.
The system
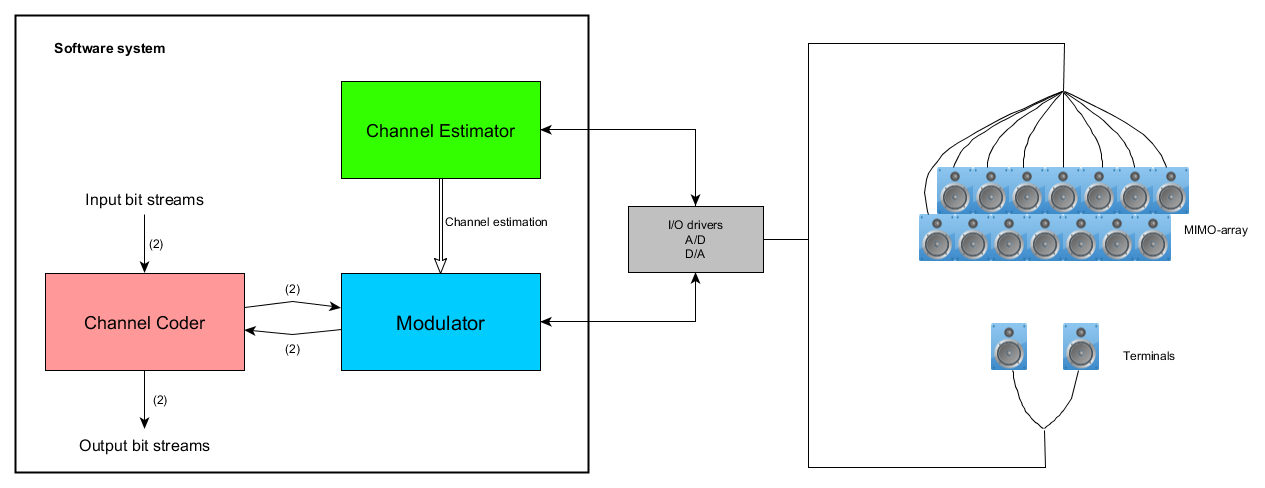 The system is split into three different sub-systems that processes all signals that are transferred or received by the microphone/loudspeaker units. Between the sub-systems and the loudspeaker/microphones there is A/D and D/A cards along with sufficient I/O drivers. The image to the rigth displays a simple overview of the system.
The system is split into three different sub-systems that processes all signals that are transferred or received by the microphone/loudspeaker units. Between the sub-systems and the loudspeaker/microphones there is A/D and D/A cards along with sufficient I/O drivers. The image to the rigth displays a simple overview of the system.
Channel estimator - Estimates the impulse responses between all loudspeaker/microphone in the MIMO array and all terminals.
Modulator - Modulates bitstreams onto real valued signals that are to be transmitted, as well as demodulating received signals.
Channel coder - Channel codes the bitstreams before they are transmitted to reduce the number bit error rate.
Results
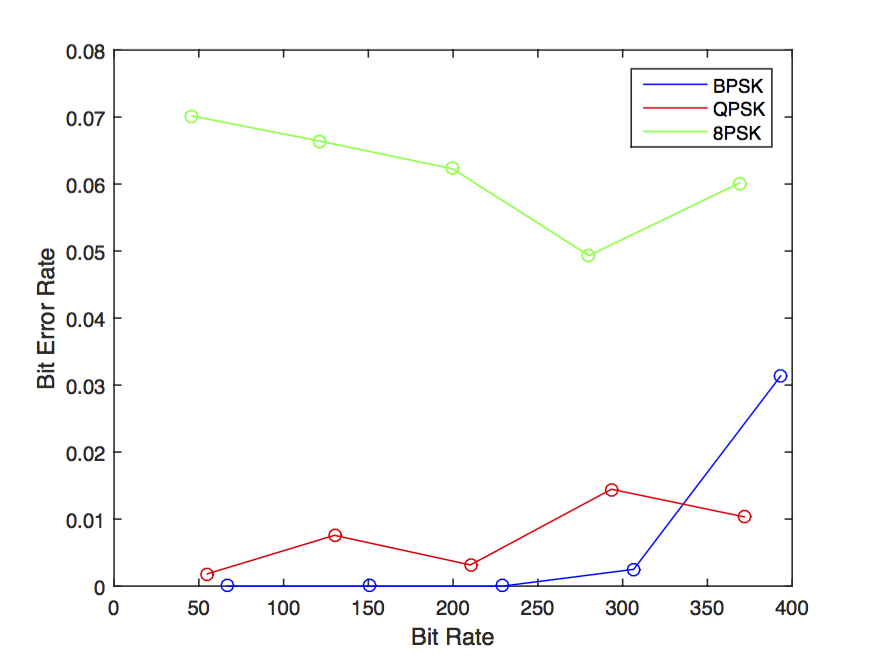 When using two terminals, as the system was originally intended to handle, it is possible to reach information bit rates of up to 300 bits per second for each terminal, with an information BER lower than 5%. The main limitations for reaching a higher BER is that the speakers sensitivity decreases rapidly for frequencies over 1600 Hz, and the fact that the A/D converter can not sample faster than 100 kHz (to be split on 16 loudspeaker/microphone units). The image to the right shows how the bit error rate increases when using higer bit rates for BPSK, QPSK and 8PSK.
When using two terminals, as the system was originally intended to handle, it is possible to reach information bit rates of up to 300 bits per second for each terminal, with an information BER lower than 5%. The main limitations for reaching a higher BER is that the speakers sensitivity decreases rapidly for frequencies over 1600 Hz, and the fact that the A/D converter can not sample faster than 100 kHz (to be split on 16 loudspeaker/microphone units). The image to the right shows how the bit error rate increases when using higer bit rates for BPSK, QPSK and 8PSK.
As mentioned earlier it is possible to transmit data to up to 4 terminals, although when doing this it is only possible to transmit data with relatively low bit rates.